Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Fujiwara, Satoru
Acta Crystallographica Section D; Structural Biology (Internet), 72(1), p.71 - 82, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:37.86(Biochemical Research Methods) -lactamase from the moderate halophile
-lactamase from the moderate halophile  sp.560 and the discovery of a Cs
sp.560 and the discovery of a Cs -selective binding site
-selective binding siteArai, Shigeki; Yonezawa, Yasushi*; Okazaki, Nobuo*; Matsumoto, Fumiko*; Shibazaki, Chie; Shimizu, Rumi; Yamada, Mitsugu*; Adachi, Motoyasu; Tamada, Taro; Kawamoto, Masahide*; et al.
Acta Crystallographica Section D, 71(3), p.541 - 554, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:50.76(Biochemical Research Methods)The crystal structure of halophilic  -lactamase from
-lactamase from  sp.560 (HaBLA) was determined using X-ray crystallography. Moreover, the locations of bound Sr
sp.560 (HaBLA) was determined using X-ray crystallography. Moreover, the locations of bound Sr and Cs
and Cs ions were identified by anomalous X-ray diffraction. The location of one Cs
ions were identified by anomalous X-ray diffraction. The location of one Cs specific binding site was identified on HaBLA even in the presence of 9-fold molar excess of Na
specific binding site was identified on HaBLA even in the presence of 9-fold molar excess of Na (90 mM Na
(90 mM Na /10 mM Cs
/10 mM Cs ). This Cs
). This Cs binding site is formed by two main-chain O atoms and an aromatic ring of a side chain of Trp. An aromatic ring of Trp interacts with Cs
binding site is formed by two main-chain O atoms and an aromatic ring of a side chain of Trp. An aromatic ring of Trp interacts with Cs by the cation-
by the cation- interaction. The observation of a selective and high-affinity Cs
interaction. The observation of a selective and high-affinity Cs binding site provides important information that is useful for designing artificial Cs
binding site provides important information that is useful for designing artificial Cs binding sites useful in bioremediation of radioactive isotopes.
binding sites useful in bioremediation of radioactive isotopes.
Tamada, Taro
Baiosaiensu To Indasutori, 63(1), p.27 - 30, 2005/01
no abstracts in English
 that stimulates DNA ligation
that stimulates DNA ligationNarumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Cui, S.*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kitayama, Shigeru; Watanabe, Hiroshi*
Molecular Microbiology, 54(1), p.278 - 285, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:132 Percentile:91.4(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)The extraordinary radiation resistance of  results from the efficient capacity of the bacterium to repair DNA double-strand breaks. By analyzing the DNA damage repair-deficient mutant, KH311, a unique radiation-inducible gene (designated
results from the efficient capacity of the bacterium to repair DNA double-strand breaks. By analyzing the DNA damage repair-deficient mutant, KH311, a unique radiation-inducible gene (designated  ) responsible for loss of radiation resistance was identified. Investigations in vitro showed that the gene product of
) responsible for loss of radiation resistance was identified. Investigations in vitro showed that the gene product of  (PprA) preferentially bound to double-stranded DNA carrying strand breaks, inhibited
(PprA) preferentially bound to double-stranded DNA carrying strand breaks, inhibited  exonuclease III activity, and stimulated the DNA end-joining reaction catalyzed by ATP-dependent and NAD-dependent DNA ligases. These results suggest that
exonuclease III activity, and stimulated the DNA end-joining reaction catalyzed by ATP-dependent and NAD-dependent DNA ligases. These results suggest that  has a radiation-induced nonhomologous end-joining repair mechanism in which PprA plays a critical role.
has a radiation-induced nonhomologous end-joining repair mechanism in which PprA plays a critical role.
Chatake, Toshiyuki; Mizuno, Nobuhiro*; Voordown, G.*; Higuchi, Yoshiki*; Arai, Shigeki; Tanaka, Ichiro; Niimura, Nobuo
Acta Crystallographica Section D, 59(Part2), p.2306 - 2309, 2003/12
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:75.55(Biochemical Research Methods)Issimilatory sulfite reductase D (DsrD) from  has been crystallized for a neutron diffraction study. The initial crystals obtained were too small for the neutron experiment. In order to obtain a larger crystal (1 mm
has been crystallized for a neutron diffraction study. The initial crystals obtained were too small for the neutron experiment. In order to obtain a larger crystal (1 mm ), a combination of two techniques was used to find the optimum crystallization conditions: a crystallization phase diagram, followed by crystal-quality assessment via X-ray diffraction. Using conditions determined in this manner, a large single crystal (1.7 mm
), a combination of two techniques was used to find the optimum crystallization conditions: a crystallization phase diagram, followed by crystal-quality assessment via X-ray diffraction. Using conditions determined in this manner, a large single crystal (1.7 mm ) of the DsrD protein was subsequently grown in D
) of the DsrD protein was subsequently grown in D O solution by the macro-seeding technique. The neutron diffraction experiment was carried out using the BIX-3 diffractometer at the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), and the diffraction data up to 2.4 AA resolution could be collected from this crystal.
O solution by the macro-seeding technique. The neutron diffraction experiment was carried out using the BIX-3 diffractometer at the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), and the diffraction data up to 2.4 AA resolution could be collected from this crystal.
Kono, Hidetoshi; Saven, J. G.*
Seibutsu Butsuri, 43(4), p.186 - 191, 2003/07
no abstracts in English
Chatake, Toshiyuki; Ostermann, A.; Kurihara, Kazuo; Parak, F.*; Niimura, Nobuo
Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics, 50(3), p.516 - 523, 2003/02
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:76.77(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)no abstracts in English
Niimura, Nobuo; Chatake, Toshiyuki
Hamon, 13(1), p.47 - 50, 2003/01
no abstracts in English
Kitao, Akio
Hamon, 12(2), p.80 - 83, 2002/04
no abstracts in English
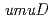 -encoded subunit of
-encoded subunit of  DNA polymerase V regulates its interactions with the
DNA polymerase V regulates its interactions with the  processivity clamp
processivity clampSutton, M. D.*; Narumi, Issei; Walker, G. C.*
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99(8), p.5307 - 5312, 2002/04
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:51.75(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The 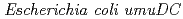 gene products (PolV) participate in both a DNA damage checkpoint control and translesion DNA synthesis. Interactions of the two
gene products (PolV) participate in both a DNA damage checkpoint control and translesion DNA synthesis. Interactions of the two 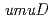 gene products, UmuD and UmuD' proteins, with components of the replicative DNA polymerase (PolIII), are important for determining which biological role the
gene products, UmuD and UmuD' proteins, with components of the replicative DNA polymerase (PolIII), are important for determining which biological role the 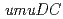 gene products will play. We have shown that UmuD possesses a higher affinity for PolIII
gene products will play. We have shown that UmuD possesses a higher affinity for PolIII  processivity clamp than does UmuD' because of the N-terminal arm of UmuD, much of which is missing in UmuD'. Futhermore, we identified specific amino acid residues of UmuD that crosslink to
processivity clamp than does UmuD' because of the N-terminal arm of UmuD, much of which is missing in UmuD'. Futhermore, we identified specific amino acid residues of UmuD that crosslink to  with a crosslinker,
with a crosslinker,  -azidoiodoacetanilide, defining the domain important for the interaction.
-azidoiodoacetanilide, defining the domain important for the interaction.
 is not involved in RecA induction following
is not involved in RecA induction following  irradiation
irradiationNarumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Kazuo
Journal of Bacteriology, 183(23), p.6951 - 6956, 2001/12
Times Cited Count:89 Percentile:83.76(Microbiology)The involvement of LexA in induction of RecA was investigated in  . As in the wild-type strain, an increase in RecA protein synthesis following
. As in the wild-type strain, an increase in RecA protein synthesis following  irradiation was detected in a
irradiation was detected in a 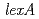 disruptant, indicating that LexA is not involved in the induction of RecA in
disruptant, indicating that LexA is not involved in the induction of RecA in  .
.
Fujiwara, Satoru
JAERI-Conf 2001-004, 228 Pages, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Hoshasen To Sangyo, (56), 55, 47 Pages, 1992/12
no abstracts in English
Asano, Masaharu; ; Kaetsu, Isao
Kobunshi Rombunshu, 39(5), p.333 - 338, 1982/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.27(Polymer Science)no abstracts in English
Asano, Masaharu; ; Kaetsu, Isao
Kobunshi Rombunshu, 39(5), p.327 - 332, 1982/00
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.85(Polymer Science)no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Atsushi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 selective binding site on a halophilic protein
selective binding site on a halophilic proteinArai, Shigeki; Adachi, Motoyasu; Tamada, Taro; Tokunaga, Hiroko*; Ishibashi, Matsujiro*; Tokunaga, Masao*; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
Because various metal ion binding sites exist on halophilic proteins, we proposed that the metal ion binding sites with an affinity to harmful metals and rare metals could be identified using X-ray crystallographic analysis in the presence of those metal ions. In this study, we attempted to identify metal ion binding sites for Sr and Cs
and Cs on a halophilic protein HaBLA derived from
on a halophilic protein HaBLA derived from 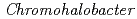 sp.560 (HaBLA) by X-ray crystallographic analysis and anomalous X-ray diffraction analysis. By these analyses, we succeeded in discovering one Cs
sp.560 (HaBLA) by X-ray crystallographic analysis and anomalous X-ray diffraction analysis. By these analyses, we succeeded in discovering one Cs binding site and three Sr
binding site and three Sr binding site for one molecule of HaBLA. Moreover, discovered Cs
binding site for one molecule of HaBLA. Moreover, discovered Cs binding site showed high Cs
binding site showed high Cs selectivity, which binds Cs
selectivity, which binds Cs even in the presence of 9-fold molar excess of Na
even in the presence of 9-fold molar excess of Na (90 mM Na
(90 mM Na / 10 mM Cs
/ 10 mM Cs ).
).
Fujiwara, Satoru; Matsuo, Tatsuhito; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru
no journal, ,
Matsuo, Tatsuhito; Arata, Toshiaki*; Oda, Toshiro*; Fujiwara, Satoru
no journal, ,
We studied the dynamics of F-actin, myosin S1 (S1), and their hydration water using quasi elastic neutron scattering (QENS). The analysis of the QENS spectra shows that the residence time of the atoms of F-actin is shorter than that of S1, and that the fraction of the "immobile" atoms is smaller for F-actin. These results suggest that more atoms fluctuate more rapidly in F-actin. The analysis of the spectra of their hydration water shows that the translational diffusion coefficient is smaller for S1 than F-actin. Whereas the residence time is similar between F-actin and S1 within the experimental errors, the rotational correlation time is smaller for F-actin. Furthermore, the translational diffusion coefficient and the rotational correlation time of the hydration water of F-actin are close to those of bulk water. These results imply that the concerted action between F-actin and its hydration water with high mobility allows F-actin to take quickly suitable conformations for S1 binding.